1
Sideroblastic Anemia 2025 Emerging Treatments and Genetic Insights
mrfrhealth edited this page 2 weeks ago
As a healthcare professional, you're likely familiar with the complexities of Sideroblastic Anemia, a rare genetic disorder characterized by the accumulation of iron in the mitochondria of red blood cells. In this blog post, we'll delve into the recent advances in diagnosis and treatment options, exploring the latest innovations and clinical applications that are transforming patient care.
Sideroblastic Anemia is a heterogeneous group of disorders, with multiple genetic mutations affecting the biosynthesis of heme. This leads to the accumulation of iron in the mitochondria, resulting in ineffective erythropoiesis and anemia. The disorder can manifest at any age, with varying degrees of severity.
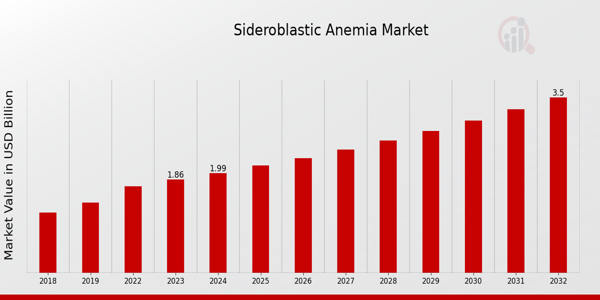
The Sideroblastic Anemia Market is set for steady growth, expected to expand from USD 1.86 Billion in 2023 to USD 3.5 Billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 7.3%. Increasing research efforts and advancements in treatment options are key drivers of market expansion.
Read the full market report here: Sideroblastic Anemia Market Report.
Diagnosing Sideroblastic Anemia can be challenging, requiring a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and genetic analysis. Recent advances in diagnostic techniques include:
-
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS): Enables simultaneous analysis of multiple genes, facilitating the identification of genetic mutations associated with Sideroblastic Anemia.
-
Mitochondrial DNA Analysis: Helps diagnose mitochondrial-related sideroblastic anemia, allowing for targeted therapeutic interventions.
-
Bone Marrow Biopsy: Provides valuable information on the morphological characteristics of erythroblasts and the presence of ringed sideroblasts.
While there is no cure for Sideroblastic Anemia, recent advances in treatment options aim to alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent complications. Some of these innovative approaches include:
-
Iron Chelation Therapy: Helps reduce iron overload, minimizing the risk of cardiac and hepatic complications.
-
Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents (ESAs): Stimulate erythropoiesis, increasing red blood cell production and reducing transfusion requirements.
-
Gene Therapy: A promising area of research, aiming to correct the underlying genetic defects responsible for Sideroblastic Anemia.
The integration of recent advances in diagnosis and treatment options has significant implications for clinical practice. Some of the key takeaways include:
-
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatment approaches to individual patients based on their specific genetic profile and clinical characteristics.
-
Multidisciplinary Care: Collaborative management involving hematologists, geneticists, and other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive care.
-
Ongoing Research: Continued investigation into the pathophysiology of Sideroblastic Anemia, exploring novel therapeutic strategies and improving existing treatments.
| Treatment Option | Mechanism of Action | Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron Chelation Therapy | Reduces iron overload | Minimizes cardiac and hepatic complications | Gastrointestinal side effects, potential for iron deficiency |
| Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents (ESAs) | Stimulates erythropoiesis | Increases red blood cell production, reduces transfusion requirements | Potential for increased risk of thrombosis, cardiovascular events |
| Gene Therapy | Corrects underlying genetic defects | Potential for cure or significant improvement in symptoms | Risks associated with gene therapy, including off-target effects and immune responses |
Sideroblastic Anemia 2025: Unlocking Recent Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment Options highlights the significant progress made in understanding and managing this complex disorder. As healthcare professionals, it's essential to stay abreast of these developments, integrating innovative diagnostic and therapeutic approaches into clinical practice to improve patient outcomes.
By continuing to advance our knowledge and explore new frontiers in Sideroblastic Anemia research, we can work towards a future where patients with this disorder can lead longer, healthier lives.